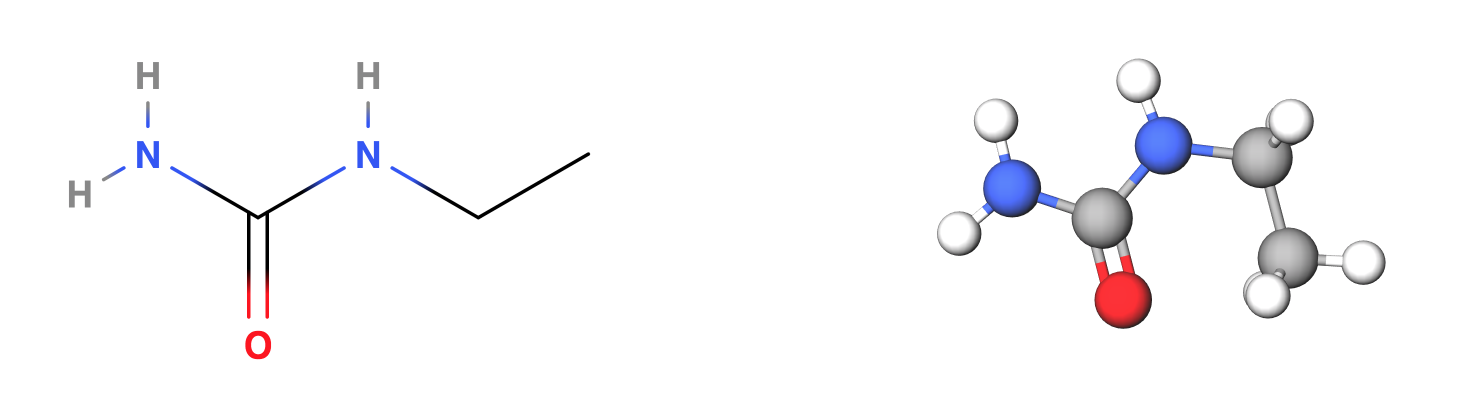The "Fiber" Diet
As Aman often says “MoS is like a chef, mixing available ingredients and making something delicious”. Well we’ll take that analogy a little further to help understand some of the “raw ingredients” a little bit better and the chemistry behind them.
TL:DR; Like the food we eat, the clothing we make is made out of familiar organic compounds like Proteins, Carbs and Fats.
A little bit on organic chemistry - it’s molecules made of Carbon (Charcoal), Hydrogen(White), Oxygen (Red) and Nitrogen (Blue) and they’re rearranged in different ways to make the building blocks of life and organic matter.
Organic Compounds in our Diet
When we think of our nutritional diet, we think of a balance of:
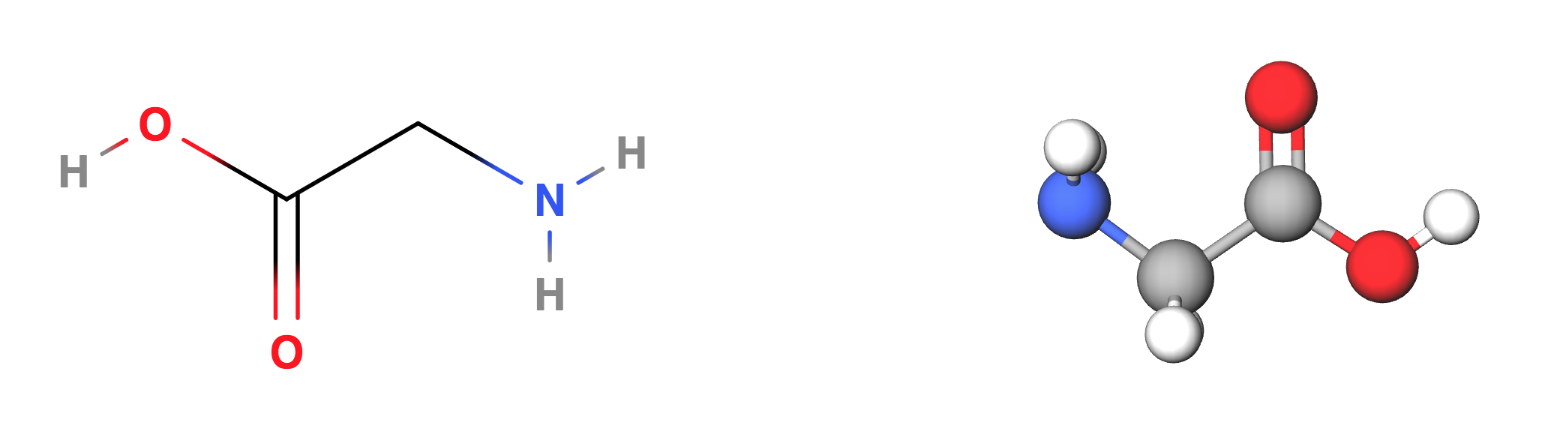
Proteins: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen (CHON)
Glycine - a common amino acid or building block of protein - chemical structure and 3D Model
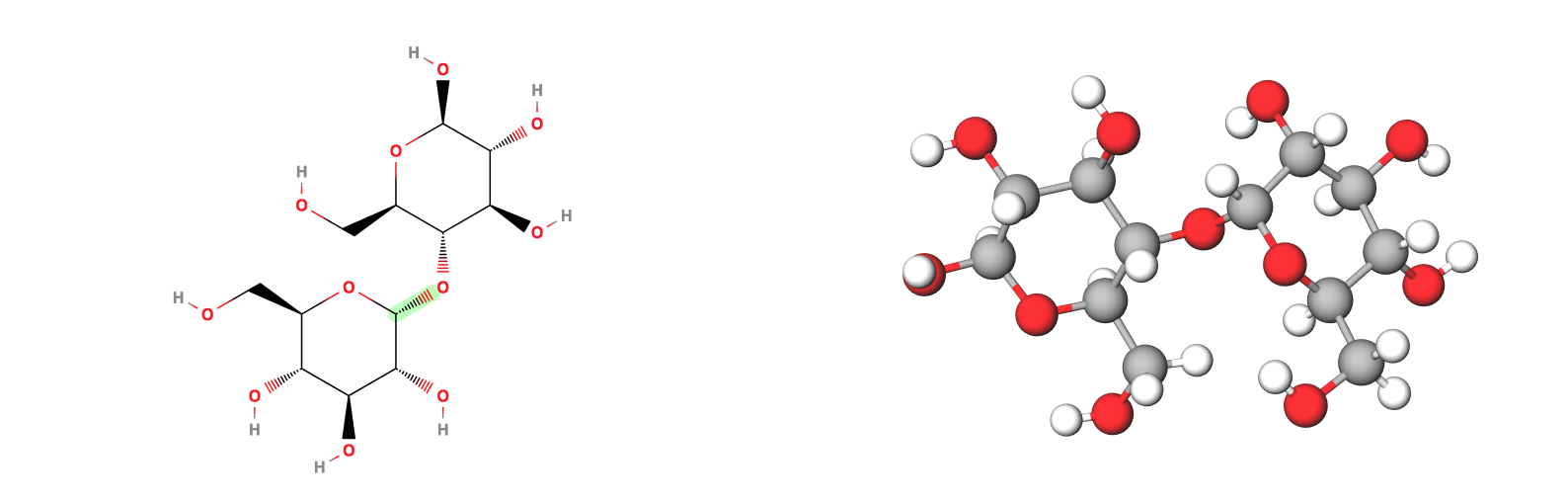
Carbohydrates: Carbo - Hydrates… Carbon Rings + Water: Carbon, (CH2O)
Maltose - a typical sugar - chemical structure and 3D Model
Fats: Fats, oils and waxes are long repeating chains with of Carbon + Hydrogen with a little bit of Oxygen (CH)
Stearic Acid - a common fatty acid - chemical structure and 3D Model
Organic Compounds in our Clothing “Fiber Diet”
Turns out that the materials that we use in our garments also fall into these categories - we just might not be able to digest all of them!
Proteins:
Wool: Wool is made of the protein Keratin.
Silk: Silk is a silk protein made by silk worms.
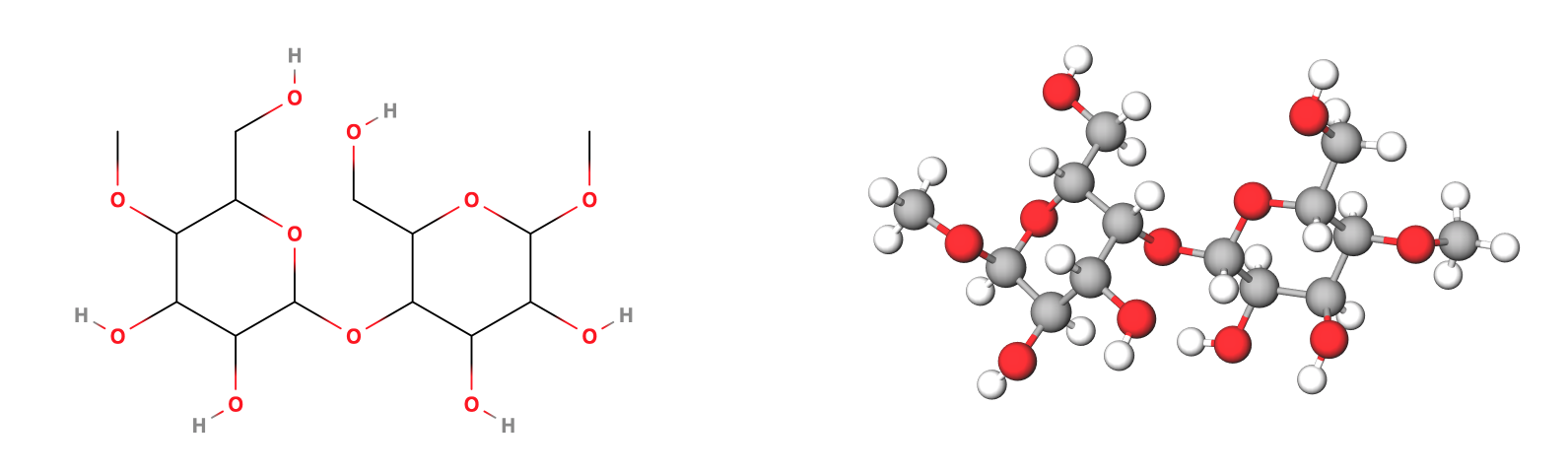
Nylon: While nylon isn’t a protein technically, it is made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen and shares similar structure and so originally it was positioned as an alternative to silk.
Nylon 6 - chemical structure and
Carbohydrates:
Cellulose - The building block of cotton and viscose
Cellulose / Cotton: Cotton is a carbohydrate, made of the sugar cellulose. That ose ending indicates its a sugar - think glucose, fructose, lactose. We just can’t digest this type of carb … but herbivores can.
Viscose aka “Rayon”: Viscose is basically is basically a shortened version of cotton. Again ose it’s sugar or carb.
Polyester: Polyester has a carbon ring and ester group similar to sugar, and is one of the reasons sugarcane can be used to create the polyester we use in the Kinetic.
Fats:
Paraffin Wax: The wax that we use in the Apollo PCMs is a hydrocarbon or “fat"
Polyurethane: We use polyurethane in many of our products to make the stretchy and or waterproof. In the lining of the Mercury Jacket, is made of 25% of bio-based polyurethane that comes from the oil from coffee beans.
Polyurethane monomer - a combination of an amine group and ethylene
When we hear about different materials, particularly synthetics - we think of them as scary molecules, when in-fact they are organic building blocks from nature just rearranged in different ways.
All images courtesy molview.org & wikipedia.org